
Blazor considered harmful
The allure of Blazor is strong. The promise of building web apps with C# instead of JavaScript is the fondest dream of .NET developers.
However, Blazor is no silver bullet. Its complexity, unconventional design decisions, and unexpected pitfalls can quickly turn development into a harrowing experience.
After my deep dive into Blazor, I can safely say that there are better alternatives out there. For example, combining MVC with HTMX helped me create an equally powerful — but simpler — web app.
Blazor: complexity made flesh
Blazor sells itself as the ideal framework for creating rich, interactive web applications with C# instead of JavaScript. This is a powerful selling point. I believed in this vision until I used Blazor to build something non-trivial.
Now that I know Blazor better than my own family, I genuinely can’t think of a single advantage Blazor has over other web frameworks. In fact, it’s riddled with pitfalls and footguns.
I now share these pitfalls with you in the hope that you will avoid falling into them.
Pessimistic re-rendering
Like most web frameworks, Razor components re-render whenever their parameters change. However, unlike most web frameworks, Blazor makes some bizarre decisions about when to re-render.
Specifically, when a component is checking whether to re-render, it takes the lazy way out and doesn’t bother to compare its complex parameters for equality. These parameters are always assumed to have changed.
This behavior is so ridiculously unintuitive that it caused me weeks of headaches as I tried to figure out where all my unnecessary re-renders were coming from.
One of the most common patterns in any web framework is running side effects when specified component props [parameters] change. For example, imagine a paginated table component in React that should fetch data only when certain props have changed. Here’s how to implement that:
useEffect(() => {
await fetchData();
}, [filters, sortColumn, sortDescending, pageNumber, maxPages]);It’s at least somewhat straightforward. Don’t get me wrong, I’m not saying React’s approach to side effects is good, because it’s not. useEffect is undoubtedly a footgun in React; it’s even been called React’s billion dollar problem. But at least it’s only a few lines of code.
This is how you achieve the same behavior in Blazor:
[Parameter] public ComplexType1 Filters { get; set; }
[Parameter] public string SortColumn { get; set; }
[Parameter] public bool SortDescending { get; set; }
[Parameter] public int PageNumber { get; set; }
[Parameter] public int MaxPages { get; set; }
private ComplexType1 _previousFilters;
private string _previousSortColumn;
private bool _previousSortDescending;
private int _previousPageNumber;
private int _previousMaxPages;
public override async Task OnParametersSetAsync()
{
await base.OnParametersSetAsync();
if (Filters != _previousFilters ||
SortColumn != _previousSortColumn ||
SortDescending != _previousSortDescending ||
PageNumber != _previousPageNumber ||
MaxPages != _previousMaxPages)
{
_previousFilters = Filters;
_previousSortColumn = SortColumn;
_previousSortDescending = SortDescending;
_previousPageNumber = PageNumber;
_previousMaxPages = MaxPages;
await FetchData();
}
}Blazor takes one of the most common patterns in all of web development and makes it a tedious mess. Here are some of the problems with Blazor’s approach:
- It takes way more code to accomplish a simple task. More surface area means more room for bugs to hide in.
- It introduces five private fields into the component. Managing this extra state increases cognitivie load and is just asking for subtle state management bugs.
- Nobody ever starts out knowing they need to write this type of code in Blazor. You only discover it after realizing you’re hitting your database ten times more often than necessary and then reading this specific section of the docs while troubleshooting the problem.
No Separation of Concerns
In traditional frontend/backend architectures for web apps, you are forced into separating the database logic from the presentation logic. This helps keep your code understandable and maintainable.
Not in Blazor.
Want to sprinkle some raw database queries into your frontend logic? Go for it, says Blazor. The result is a tangled mess of behavior that is difficult to maintain. Sure, you can avoid this problem manually by creating DTOs or a service layer, or whatever. But the framework itself doesn’t encourage a good architecture.
Blazor Server is a subpar user experience
Blazor Server is a rendering mode of Blazor in which the entire application state lives on the server. Whenever the user interacts with the site, the server renders the updated HTML, compares it to the previous HTML, and sends the difference between them to the user via a SignalR connection.
When I first started working with Blazor Server, I expected these constant round trips to the server to feel frustratingly laggy. However, I was pleasantly surprised by how snappy it felt most of the time.
Unfortunately, it only feels snappy with a solid internet connections. When a connection is spotty (or when server resources are maxed out), the entire webpage freezes.
It is incredibly frustrating when you can’t even open a dropdown menu because your connection is slow!
Too easy to introduce unnecessary state
Most web frameworks these days are “functional” in nature: they take in props and deterministically render HTML based on that state. If you need internal state, you can opt in. I find this functional approach extremely useful because state is one of the largest sources of complexity and bugs in software.
Minimizing state also makes applications easier to reason about, since you don’t have to hold as many concepts in your head at the same time.
Blazor sort of follows the trend of being functional, but mostly doesn’t. Like other frameworks, it has props [parameters], but that’s where the similarities end. As a C# framework, Blazor inherits (heh) much of its design from object oriented programming.
One of the consequences of this design is that Blazor components have mutable state which can be modified by the component itself or by its parent. This can lead to weird behavior and bugs, especially when dealing with asynchronous operations or event handlers.
Data binding is incomprehensibly intricate
Data binding is another thing that you would expect your web framework to handle out of the box, right?
Wrong.
While writing my Blazor app, I ran into an issue where sometimes the characters in an input field would get deleted as I typed them. Turns out it was because I wasn’t using Blazor’s special data binding syntax: @bind.
However, as I tried to learn the “right” way to do data binding, I discovered that @bind is a rabbit hole so deep that you will never climb out.
Please don’t ask me to elaborate further on when you’re supposed to use @bind, @bind:get, @bind:set, and when you’re not supposed to use any of them. I will probably cry.
Lacks JavaScript features
Blazor sells itself as a way to write web apps without JavaScript.
This is a false promise.
Blazor cannot do many things without JavaScript. Scrolling a DOM element into view is an example.
To work around this limitation, you can:
- Write JavaScript code
- Expose it to your C# code
- Call it using
JSInterop
This complicates what should be a simple task. Essentially, you’re hopping between two languages and troubleshooting both, doubling the work and points of failure.
So what’s the alternative?
If Blazor isn’t all it’s cracked up to be, what should you use instead?
The most obvious replacement would be a JavaScript-based framework like React. As shown in the example code above, React doesn’t have the pessimistic re-rendering problem or the multi-language interop problem.
However, for the most complexity-averse among you, I propose a simpler solution: MVC + HTMX.
MVC (Model View Controller) is the boring, old-school way to write web applications in C#. As such, it is much simpler than Blazor.
With MVC, you don’t have to manage a complex nested hierarchy of components with complex lifecycles, parameters, and weird rendering quirks. It’s just simple, stateless requests and responses.
It’s also less powerful. This is often good. But if you’re worried about giving up Blazor Components, MVC comes with a ton of helpful features like layouts, tag helpers, partial views, and view components that can help a lot with elimininating duplicated HTML.
In my experience, the majority of Razor components do nothing but render static HTML. In these cases, MVC can do the same thing but even more easily, since you don’t have to worry about component lifecycles.
However, sometimes you really need more power. One possibility is to combine Blazor and MVC in the same project. This is a valid approach, but I prefer to avoid Blazor entirely.
That’s where HTMX comes in.
HTMX gives us extra power without sacrificing simplicity. Think of it like HTML on steroids. As its front page says, it enables you to “build modern user interfaces with the simplicity and power of hypertext.” No JavaScript required.
Here’s a simple example of how MVC + HTMX works. Let’s imagine you have a website with a navbar.
<a href="/page1">Page 1</a>
<a href="/page2">Page 2</a>Now let’s say you don’t want to reload the entire page every time the user clicks a link. Instead, you want to swap out only the relevant section of the page.
This is super easy with HTMX.
<a href="/page1" hx-get="/page1">Page 1</a>
<a href="/page2" hx-get="/page2">Page 2</a>The navbar links should have hx-get on them with the same link. The controller action will check if the HX-Trigger header is set, and if so, it only sends a section of the page instead of the whole thing.
public IActionResult MyPage()
{
if (Request.Headers.ContainsKey("HX-Trigger"))
{
return PartialView("_PageContent");
}
return View();
}The result feels just like a single page app!
Since the value HX-Trigger is customizable in HTMX, this approach can be expanded upon by examining the contents of HX-Trigger and returning different sections of the page based on which element triggered the request.
Experimenting with MVC + HTMX
As a proof of concept, I spent two days rewriting a section of an enterprise application from Blazor to MVC + HTMX. The final product was functionally identical to the Blazor version but required 62% less code to implement.
Not only is it possible to use MVC + HTMX in place of Blazor without any functionality compromises, but the end result is a lot simpler!
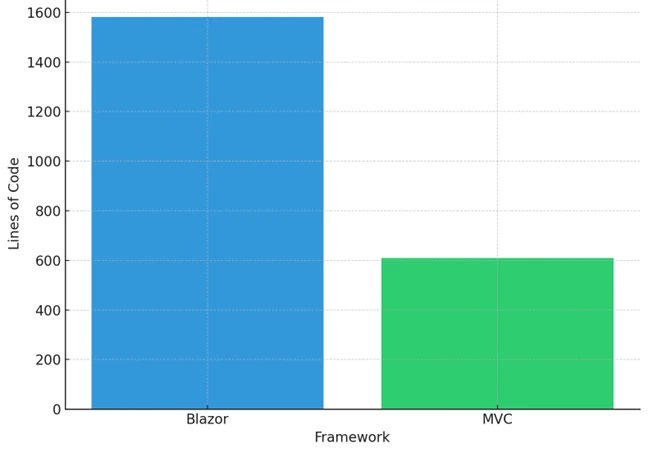
The code reduction came mainly from deleting:
- Parameter-passing boilerplate
- Component state management logic
- Component lifecycle management logic
I found that many Razor components were not doing anything particularly complicated and were easy to replace with tag helpers, which reduced the line count significantly.
Granted, lines of code aren’t everything. I’ll take a slightly verbose function over a code-golfed one-liner any day. But in this case, I found the MVC + HTMX code to be both shorter and more readable.
Functionality is an asset, but code is a liability
- Ted Dziuba, Taco Bell Programming
Conclusion
So, what’s the moral of the story?
By choosing a simpler solution than Blazor, you will enjoy faster development. Faster development will result in reduced cost of new features and increased responsiveness to customer needs.
Speaking from personal experience, avoiding Blazor will also result in less burnout.
If nothing else, I hope this post helps some poor Blazor developer from falling into the same pitfalls that I did.
May your day be filled with simple problems and equally simple solutions 🙏